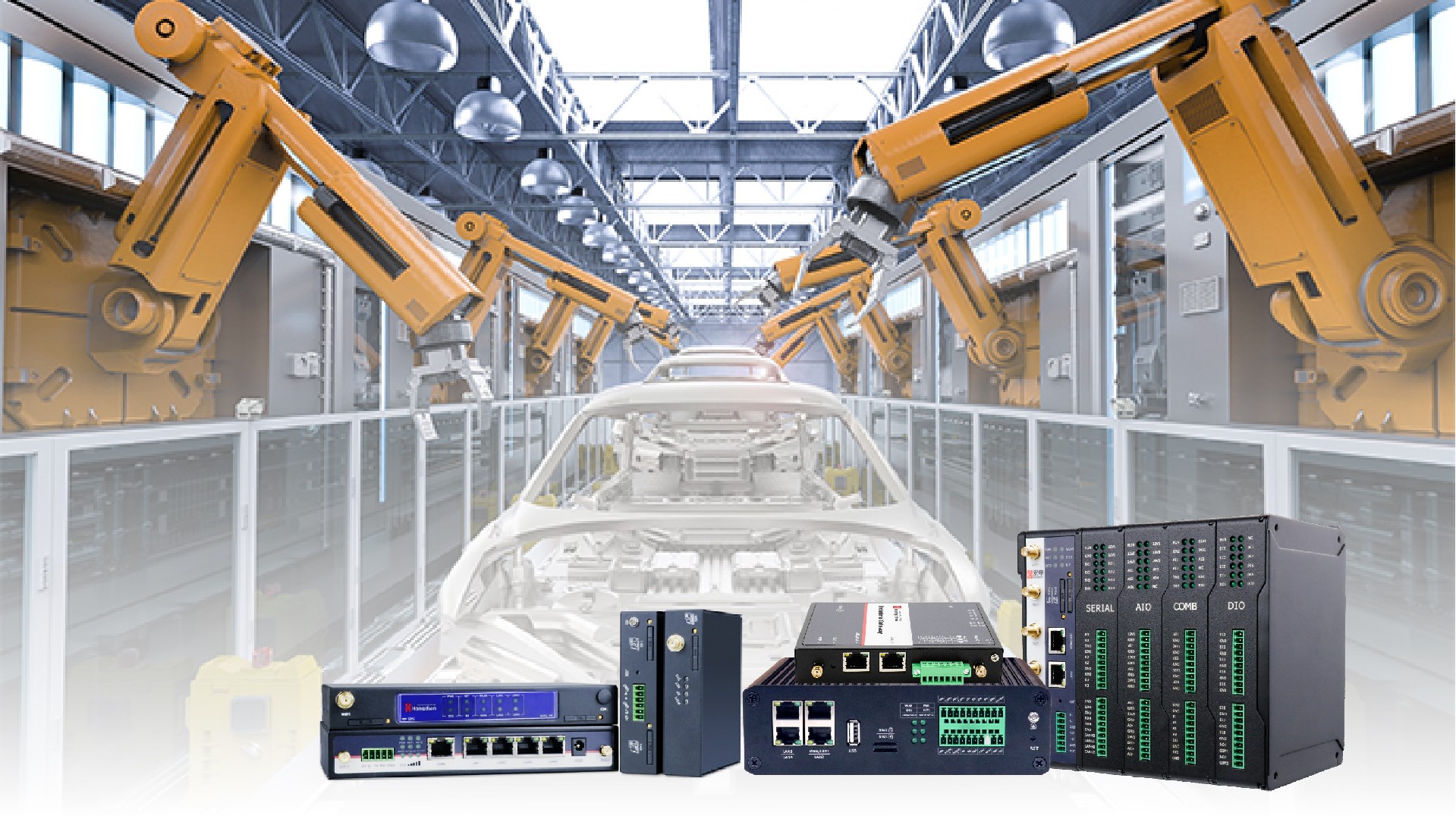
Introduction: Why Industrial Connectivity Needs a New Approach
Industrial operations today are no longer confined to a single factory or control room.
Across manufacturing, energy, logistics, and utilities, industrial assets are increasingly distributed across remote sites, machines, and facilities.
However, traditional industrial networking models struggle to keep up with this shift:
-
Wired infrastructure is costly or unavailable at remote sites
-
Legacy VPNs lack scalability and centralized visibility
-
OT data must be securely transmitted without impacting operational stability
To support modern IIoT deployments, industrial connectivity must be secure, flexible, and centrally manageable—from the edge to the cloud.
Rethinking Industrial Connectivity for Distributed IIoT Systems
Rather than treating networking as isolated point-to-point connections, modern industrial environments require a system-level connectivity architecture that connects:
-
Remote machines and controllers
-
Distributed industrial sites
-
Central supervisory and management platforms
This approach focuses on three core layers:
-
Reliable edge connectivity
-
Secure data transmission
-
Centralized network orchestration
Together, these layers form the foundation of scalable IIoT networking.
A Layered Industrial Connectivity Solution
1. Edge Connectivity: Always-On Access for Remote Sites & Machines
At the field level, industrial routers and gateways provide always-on cellular connectivity for remote machines and sites.
Key capabilities include:
-
4G/5G cellular access for locations without fixed broadband
-
Support for Ethernet, RS232/RS485, and industrial interfaces
-
Secure VPN tunnels to connect machines directly to supervisory networks
This enables industrial equipment to remain connected regardless of location or infrastructure constraints.
2. Industrial Protocol Gateways: Bridging OT Data to IT & Cloud
Industrial environments rely on diverse protocols and legacy equipment.
Industrial protocol gateways play a critical role by:
-
Collecting data from PLCs, sensors, and controllers
-
Supporting protocols such as Modbus, OPC UA, BACnet, IEC 61850, and Profinet
-
Pre-processing data at the edge before transmission
With built-in cellular connectivity, gateways can securely deliver OT data to enterprise systems or cloud platforms using MQTT, HTTPS, or TCP/UDP—without complex wiring.
3. Centralized Connectivity Management with IIoT SD-WAN
As the number of connected sites grows, managing networks individually becomes inefficient and error-prone.
An IIoT SD-WAN–based connectivity management platform enables:
-
Centralized orchestration of distributed industrial networks
-
Secure, segmented data tunnels between sites and headquarters
-
Unified visibility into network status, performance, and availability
By abstracting network complexity, SD-WAN allows industrial teams to scale deployments while maintaining control and security.
Key Benefits for Industrial Operators
By adopting a layered industrial connectivity architecture, organizations can achieve:
-
Faster deployment of new industrial sites and machines
-
Improved network reliability through cellular redundancy
-
Enhanced security with encrypted tunnels and network isolation
-
Lower operational costs via centralized management and reduced site visits
Most importantly, connectivity becomes an enabler—not a bottleneck—for industrial digital transformation.
Enabling Industrial Connectivity with Hongdian Solutions
Hongdian provides a comprehensive portfolio of industrial cellular routers, protocol gateways, and IIoT SD-WAN solutions designed for harsh environments and distributed deployments.
These solutions support industrial users in building secure, scalable, and future-ready connectivity across remote sites and machines.